Acrylic Polymers
Acyclic alcohol derivatives (halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated)
Acyclic Hydrocarbons
Air Conditioners
Air Pumps
Aircraft Launch Gear
Aircraft parts for spacecraft, UAVs, and ground equipment
Aldehydes, cyclic polymers, and paraformaldehyde
Aluminium Bars
Aluminium Cans
Aluminium Foil
Aluminium Gas Containers
Aluminium Housewares
Aluminium Pipe Fittings
Aluminium Pipes
Aluminium Plating
Aluminium Powder
Aluminium Structures
Aluminium Wire
Amine Compounds
Amino-resins
Animal Extracts
Animal Food
Animal Meal and Pellets
Animal or Vegetable Fertilizers
Antibiotics
Antifreeze
Antiknock
Aqueous Paints
Architectural Plans
Artificial Filament Sewing Thread
Artificial Filament Yarn Woven Fabric
Artificial Graphite
Artificial Textile Machinery
Artificial Vegetation
Artistry Paints
Asbestos Cement Articles
Asphalt Mixtures
Audio Alarms
Audio and Video Recording Accessories
Awnings, Tents, and Sails
Baby Carriages
Baked Goods
Ball Bearings
Bandages
Barbed Wire
Base Metal Watches
Basketwork
Bathroom Ceramics
Batteries
Beauty Products
Bedspreads
Bells and Other Metal Ornaments
Bi-Wheel Vehicle Parts
Bicycles, delivery tricycles, other cycles
Binoculars and Telescopes
Bitumen and asphalt
Blank Audio Media
Blankets
Boat Propellers
Boiler Plants
Book-binding Machines
Broadcasting Accessories
Broadcasting Equipment
Brochures
Building Stone
Buses
Calculators
Calendars
Cameras
Candles
Carbon
Carbon Paper
Carbon-based Electronics
Carboxyamide Compounds
Carboxylic Acids
Carded Wool or Animal Hair Fabric
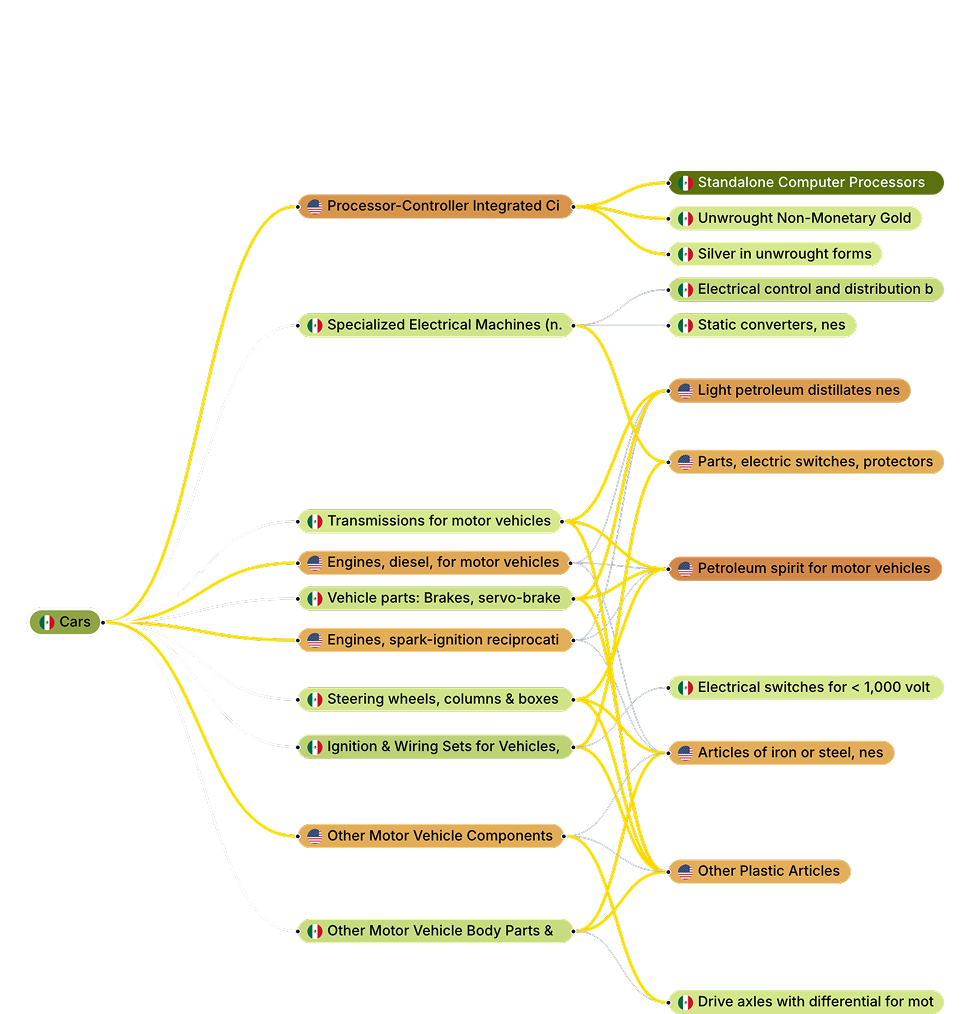
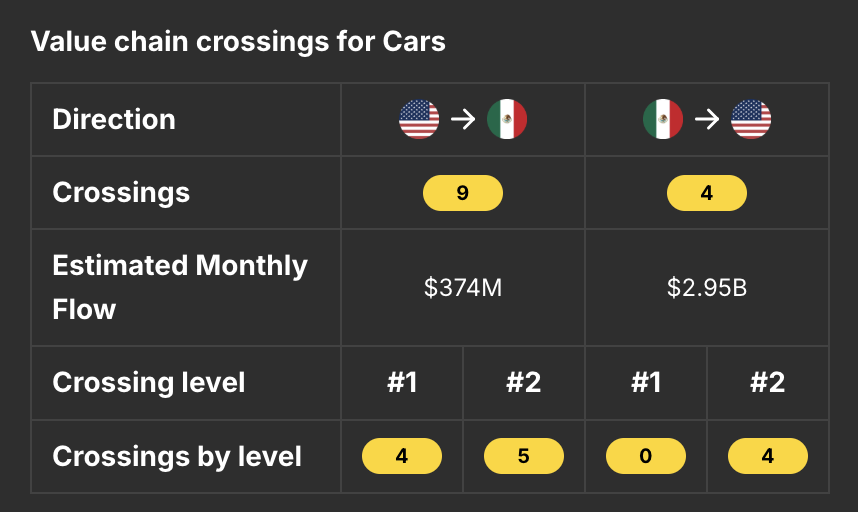
Cars
Cast Iron Pipes
Cast or Rolled Glass
Casting Machines
Cathode Tubes
Cellulose Fibers Paper
Cement
Cement Articles
Central Heating Boilers
Centrifuges
Ceramic Bricks
Ceramic Pipes
Ceramic Tableware
Cereal Flours
Cereal Meal and Pellets
Cermets
Chamois (including combination chamois) leather
Chemical Analysis Instruments
Children's Picture Books
Chocolate
Cigarette Paper
Clays
Cleaning Products
Clock Cases and Parts
Coal Tar Oil
Coated Flat-Rolled Iron
Coated Metal Soldering Products
Coated Textile Fabric
Cobalt
Coffee and Tea Extracts
Coin
Cold-Rolled Iron
Combed Wool or Animal Hair Fabric
Combustion Engines
Compasses
Composite Paper
Composition leather with a basis of leather or leather fibre
Compounded Unvulcanised Rubber
Computers
Confectionery Sugar
Conveyor Belt Textiles
Cooking Hand Tools
Copper Alloys
Copper Bars
Copper Fasteners
Copper Foil
Copper Housewares
Copper Pipe Fittings
Copper Pipes
Copper Plating
Copper Powder
Copper Wire
Corrugated Paper
Cranes
Curbstones
Cutlery Sets
Cutting Blades
Cyclic Alcohols
Cyclic Hydrocarbons
Dairy Machinery
Dashboard Clocks
Decals
Delivery Trucks
Densified Wood
Dental Products
Detonating Fuses
Developed Exposed Photographic Material
Diazo, Azo or Aoxy Compounds
Disc Chemicals for Electronics
Dithionites and Sulfoxylates
Documents of title (bonds etc) and unused stamps
Drafting Tools
Drilling Machines
Drones
Dyeing Finishing Agents
Electric Batteries
Electric Filament
Electric Furnaces
Electric Generating Sets
Electric Heaters
Electric Motor Parts
Electric Motors
Electric Musical Instruments
Electric Soldering Equipment
Electrical Capacitors
Electrical Control Boards
Electrical Ignitions
Electrical Lighting and Signalling Equipment
Electrical Parts
Electrical Power Accessories
Electrical Resistors
Electrical Transformers
Electromagnets
Embroidery
Engine Parts
Epoxides
Essential Oils
Ethers
Ethylene Polymers
Excavation Machinery
Eyewear
Eyewear and Clock Glass
Eyewear Frames
Fake Hair
Felt
Felt Carpets
Felt Machinery
Felt or Coated Fabric Garments
Ferroalloys
Filing Cabinets
Fire Extinguishers Preparations
Fireworks
Flat Flat-Rolled Steel
Flat-Rolled Iron
Flat-Rolled Stainless Steel
Flavored Water
Flexible Metal Tubing
Float Glass
Footwear Parts
Forage Crops
Forging Machines
Fork-Lifts
Friction Material
Fruit Juice
Fruit Pressing Machinery
Furskin Apparel
Garden Tools
Garments of Impregnated Fabric
Gas and Liquid Flow Measuring Instruments
Gas Turbines
Gaskets
Gauze
Gimp Yarn
Glands and Other Organs
Glass Beads
Glass Bottles
Glass Bricks
Glass Bulbs
Glass Fibers
Glass Mirrors
Glass with Edge Workings
Glass Working Machines
Glaziers Putty
Glues
Glycerol
Gold Clad Metals
Gravel and Crushed Stone
Ground Nut Oil
Gum Coated Textile Fabric
Hair Products
Hair Trimmers
Halogenated hydrocarbon mixtures
Halogenated Hydrocarbons
Hand Saws
Hand Tools
Hand-Woven Rugs
Handkerchiefs
Hard Liquor
Hard Rubber
Harvesting Machinery
Hat Forms
Hat Shapes
Hats
Headbands and Linings
Heavy Mixed Woven Cotton
Heavy Pure Woven Cotton
Heavy Synthetic Cotton Fabrics
High-voltage Protection Equipment
Hormones
Horsehair Fabric
Hose Piping Textiles
Hot-Rolled Iron
Hot-Rolled Iron Bars
House Linens
Household Washing Machines
Hydraulic Brake Fluid
Hydraulic Turbines
Hydrometers
Ice Cream
Image Projectors
Imitation Jewellery
Industrial Fatty Acids, Oils and Alcohols
Industrial Food Preperation Machinery
Industrial Furnaces
Industrial Printers
Inedible Fats and Oils
Inhalable tobacco/nicotine products
Ink
Inorganic Salts
Instructional Models
Insulated Wire
Insulating Glass
Integrated Circuits
Interchangeable Tool Parts
Interior Decorative Glassware
Iron Anchors
Iron Blocks
Iron Chains
Iron Cloth
Iron Fasteners
Iron Gas Containers
Iron Housewares
Iron Ingots
Iron Nails
Iron Pipe Fittings
Iron Pipes
Iron Powder
Iron Radiators
Iron Railway Products
Iron Reductions
Iron Sewing Needles
Iron Sheet Piling
Iron Springs
Iron Stovetops
Iron Structures
Iron Toiletry
Iron Wire
Jams
Jewellery
Jute Woven Fabric
Kaolin Coated Paper
Ketones and Quinones
Knit Active Wear
Knit Babies' Garments
Knit Gloves
Knit Men's Coats
Knit Men's Shirts
Knit Men's Suits
Knit Men's Undergarments
Knit Socks and Hosiery
Knit Sweaters
Knit T-shirts
Knit Women's Coats
Knit Women's Shirts
Knit Women's Suits
Knit Women's Undergarments
Knitted Hats
Knitted or crocheted fabrics of a width exceeding 30 cm
Knitted or crocheted fabrics of a width not exceeding 30 cm
Knitting Machine Accessories
Knitting Machines
Knives
Knotted Carpets
Kraft Paper
Labels
Laboratory Ceramic Ware
Laboratory Glassware
Laboratory Reagents
Lake Pigments
Large Aluminium Containers
Large Coated Flat-Rolled Iron
Large Construction Vehicles
Large Flat-Rolled Iron
Large Flat-Rolled Stainless Steel
Large Iron Containers
LCDs
Lead Sheets
Leather Apparel
Leather Footwear
Leather further prepared after tanning or crusting of animals (other than ovine)
Leather Machinery
Leather of Other Animals
Legume Flours
Letter Stock
Lifting Machinery
Light Mixed Woven Cotton
Light Pure Woven Cotton
Light Rubberized Knitted Fabric
Light Synthetic Cotton Fabrics
Linoleum
Liquid Dispersing Machines
Liquid Fuel Furnaces
Liquid Pumps
Locomotive Parts
Looms
Low-voltage Protection Equipment
Lubricating Products
Machinery Having Individual Functions
Machinery parts, not containing electrical connectors, insulators, coils, contacts or other electrical features, not specified or included elsewhere in this Chapter.
Machines and apparatus of a kind used solely or principally for the manufacture of semiconductor boules or wafers, semiconductor devices, electronic integrated circuits or flat panel displays
Magnesium
Malt Extract
Manganese
Maps
Margarine
Medical Instruments
Metal Finishing Machines
Metal Insulating Fittings
Metal Lathes
Metal Molds
Metal Mountings
Metal Office Supplies
Metal Pickling Preparations
Metal Signs
Metal Stoppers
Metal-Clad Products
Metal-Rolling Mills
Metallic Fabric
Metallic Yarn
Metalworking Machine Parts
Metalworking Machines
Metalworking Transfer Machines
Micro-Organism Culture Preparations
Microphones and Headphones
Microscopes
Mill Machinery
Milling Stones
Mirrors and Lenses
Mixed Mineral or Chemical Fertilizers
Molybdenum
Monofilament
Motor vehicle (8701 to 8705) chassis fitted with engine
Motor vehicles; parts and accessories (8701 to 8705)
Motor-working Tools
Motorcycles and cycles
Musical Instrument Parts
Narrow Woven Fabric
Navigation Equipment
Neck Ties
Newspapers
Nickel Bars
Nickel Pipes
Nickel Sheets
Nitrogen Heterocyclic Compounds
Nitrogenous Fertilizers
Non-Knit Active Wear
Non-Knit Babies' Garments
Non-Knit Gloves
Non-Knit Men's Coats
Non-Knit Men's Shirts
Non-Knit Men's Suits
Non-Knit Men's Undergarments
Non-Knit Women's Coats
Non-Knit Women's Shirts
Non-Knit Women's Suits
Non-Knit Women's Undergarments
Non-Mechanical Removal Machinery
Non-optical Microscopes
Non-powered Aircraft
Non-Retail Artificial Filament Yarn
Non-Retail Artificial Staple Fibers Sewing Thread
Non-Retail Artificial Staple Fibers Yarn
Non-Retail Carded Wool Yarn
Non-Retail Combed Wool Yarn
Non-Retail Mixed Cotton Yarn
Non-Retail Pure Cotton Yarn
Non-Retail Synthetic Filament Yarn
Non-Retail Synthetic Staple Fibers Yarn
Non-woven Textiles
Nonaqueous Paints
Nonaqueous Pigments
Nuclear Reactors
Office Machine Parts
Oil Seed Flower
Opto-Electric Instrument Parts
Organic Composite Solvents
Organo-Sulfur Compounds
Ornamental Ceramics
Ornamental Trimmings
Orthopedic Appliances
Oscilloscopes
Other Agricultural Machinery
Other Aluminium Products
Other Articles of Twine and Rope
Other Carbon Paper
Other Carpets
Other Cast Iron Products
Other Ceramic Articles
Other Clocks
Other Clocks and Watches
Other Cloth Articles
Other Coloring Matter
Other Construction Vehicles
Other Copper Products
Other Cotton Fabrics
Other Cutlery
Other Domestic Electric Housewares
Other Edible Preparations
Other Electrical Machinery
Other Engines
Other Fermented Beverages
Other Firearms
Other Floating Structures
Other Footwear
Other Glass Articles
Other Hand Tools
Other Headwear
Other Heating Machinery
Other Iron Bars
Other Iron Products
Other Knit Clothing Accessories
Other Knit Garments
Other knitted or crocheted fabrics.
Other Large Iron Pipes
Other Lead Products
Other Leather Articles
Other Measuring Instruments
Other Metal Fasteners
Other Metals
Other Musical Instruments
Other Nickel Products
Other Nitrogen Compounds
Other Non-Knit Clothing Accessories
Other Non-Metal Removal Machinery
Other Office Machines
Other Organic Compounds
Other Organo-Inorganic Compounds
Other Paints
Other Paper Machinery
Other Plastic Products
Other Plastic Sheetings
Other Precious Metal Products
Other Prepared Meat
Other Printed Material
Other Processed Fruits and Nuts
Other Processed Vegetables
Other Pure Vegetable Oils
Other Rubber Products
Other Sea Vessels
Other Small Iron Pipes
Other Stainless Steel Bars
Other Steel Bars
Other Sugars
Other Synthetic Fabrics
Other Uncoated Paper
Other Vegetable Fibers Fabric
Other Vegetable Fibers Yarn
Other Vegetable Oils
Other Vegetable Products
Other Vegetable Residues and Waste
Other Women's Undergarments
Other Wood Articles
Other Zinc Products
Oxygen Amino Compounds
Oxygen Heterocyclic Compounds
Packaged Medicaments
Packaged Sewing Sets
Packing Bags
Padlocks
Paper Containers
Paper Labels
Paper Notebooks
Paper Pulp Filter Blocks
Paper Spools
Papermaking Machines
Particle Board
Pasta
Pastes and Waxes
Pearl Products
Perfume Plants
Perfumes
Pesticides
Petroleum Coke
Petroleum Jelly
Petroleum Resins
Pharmaceutical Rubber Products
Phenol Derivatives
Phenols
Phosphatic Fertilizers
Phosphoric Acid
Phosphoric Esters and Salts
Photo Lab Equipment
Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Film
Photographic Paper
Photographic Plates
Pianos
Pile Fabric
Pitch Coke
Plaiting Products
Plaster Articles
Plastic Building Materials
Plastic Coated Textile Fabric
Plastic Floor Coverings
Plastic Housewares
Plastic Lids
Plastic Pipes
Plastic Wash Basins
Platinum Clad Metals
Plywood
Polishes and Creams
Polyacetals
Polyamide Fabric
Polyamides
Polycarboxylic Acids
Polymer Ion-Exchangers
Porcelain Tableware
Portable Lighting
Postcards
Potassic Fertilizers
Potato Flours
Precious Metal Compounds
Precious Metal Scraps
Precious Metal Watches
Precious Stone Dust
Prepared Cereals
Prepared Explosives
Prepared Pigments
Prepared Rubber Accelerators
Prepr binder for foundry
Print Production Machinery
Printed Circuit Boards
Processed Artificial Staple Fibers
Processed Cereals
Processed Crustaceans
Processed Fish
Processed Synthetic Staple Fibers
Processed Tobacco
Propylene Polymers
Pulley Systems
Quaternary Ammonium Salts and Hydroxides
Quicklime
Quilted Textiles
Radio Receivers
Railway Cargo Containers
Railway Freight Cars
Railway Maintenance Vehicles
Railway Track Fixtures
Raw Aluminium
Raw Iron Bars
Raw Lead
Raw Plastic Sheeting
Raw Zinc
Razor Blades
Reaction and Catalytic Products
Reclaimed Rubber
Recreational Boats
Refined Copper
Refined Petroleum
Refractory Bricks
Refractory Cements
Refractory Ceramics
Refrigerators
Residual products of the chemical or allied industries
Retail Artificial Filament Yarn
Retail Artificial Staple Fibers Yarn
Retail Cotton Yarn
Revolution Counters
Rock Wool
Rolled Tobacco
Rolling Machines
Roofing Tiles
Rubber Apparel
Rubber Belting
Rubber Footwear
Rubber Inner Tubes
Rubber Pipes
Rubber Sheets
Rubber Textile Fabric
Rubber Textiles
Rubber Thread
Rubber Tires
Rubberworking Machinery
Saddlery
Safes
Safety Glass
Sauces and Seasonings
Sausages
Scarves
Scented Mixtures
Scissors
Scrap Aluminium
Scrap Iron
Seed Oils
Self-adhesive Plastics
Semi-Finished Iron
Semiconductor Devices
Sewing Machines
Shaped Paper
Shaped Wood
Shaving Products
Sheet Music
Signaling Glassware
Silicates
Silver Clad Metals
Small Iron Containers
Soap
Soil Preparation Machinery
Soldering and Welding Machinery
Sound Recording Equipment
Soups and Broths
Soybean Oil
Spark-Ignition Engines
Special Pharmaceuticals
Special purpose motor vehicles
Stainless Steel Ingots
Stainless Steel Wire
Starches
Steam Boilers
Steam Turbines
Steel Ingots
Steel Wire
Stone Processing Machines
Stone Working Machines
Stranded Aluminium Wire
Stranded Copper Wire
Stranded Iron Wire
String Instruments
Sugar Preserved Foods
Sulfates
Sulfites
Sulfonamides
Sulfonated, Nitrated or Nitrosated Hydrocarbons
Surveying Equipment
Synthetic Coloring Matter
Synthetic Fabrics
Synthetic Filament Tow
Synthetic Filament Yarn Woven Fabric
Synthetic Monofilament
Synthetic Rubber
Synthetic Tanning Extracts
Tanks and Armored vehicles
Tanned Equine and Bovine Hides
Tantalum
Telephones
Tensile Testing Machines
Terry Fabric
Textile Fiber Machinery
Textile Footwear
Textile Processing Machines
Textile Scraps
Textile Wall Coverings
Textile Wicks
Textiles for technical uses
Therapeutic Appliances
Thermostats
Time Recording Instruments
Time Switches
Tin Bars
Tissue
Titanium
Tobacco Processing Machines
Toilet Paper
Tool Plates
Tool Sets
Tractors
Traffic Signals
Trailers and semi-trailers, not mechanically propelled vehicles
Transmissions
Trunks and Cases
Tufted Carpets
Tulles and Net Fabric
Tungsten
Twine and Rope
Twine, cordage or rope; knotted netting, made up fishing nets and other made up nets, of textile materials
Umbrella and Walking Stick Accessories
Umbrellas
Uncoated Paper
Unglazed Ceramics
Unpackaged Medicaments
Unsaturated Acyclic Monocarboxylic Acids
Unvulcanised Rubber Products
Used Clothing
Used Rubber Tires
Utility Meters
Vaccines, blood, antisera, toxins and cultures
Vacuum Cleaners
Valves
Vegetable Alkaloids
Vegetable Fiber
Vegetable or Animal Dyes
Vegetable Parchment
Vegetable Saps
Vehicle Bodies (including cabs) for the motor vehicles (8701 to 8705)
Vending Machines
Veneer Sheets
Video Cameras
Video Displays
Video Recording Equipment
Vinyl Chloride Polymers
Vitamins
Wadding
Walking Sticks
Wallpaper
Warp knit fabrics (including those made on galloon knitting machines)
Washing and Bottling Machines
Watch Cases and Parts
Watch Movements
Watch Straps
Water and Gas Generators
Waterproof Footwear
Waxes
Wheat Flours
Wheelchairs
Window Dressings
Wood Barrels
Wood Carpentry
Wood Crates
Wood Fiberboard
Wood Frames
Wood Kitchenware
Wood Ornaments
Wood Stakes
Wooden Tool Handles
Woodworking machines
Work Trucks
Woven Fabric of Synthetic Staple Fibers
Woven Fabrics
Wrenches
X-Ray Equipment
Yeast
Zinc Powder
Zinc Sheets